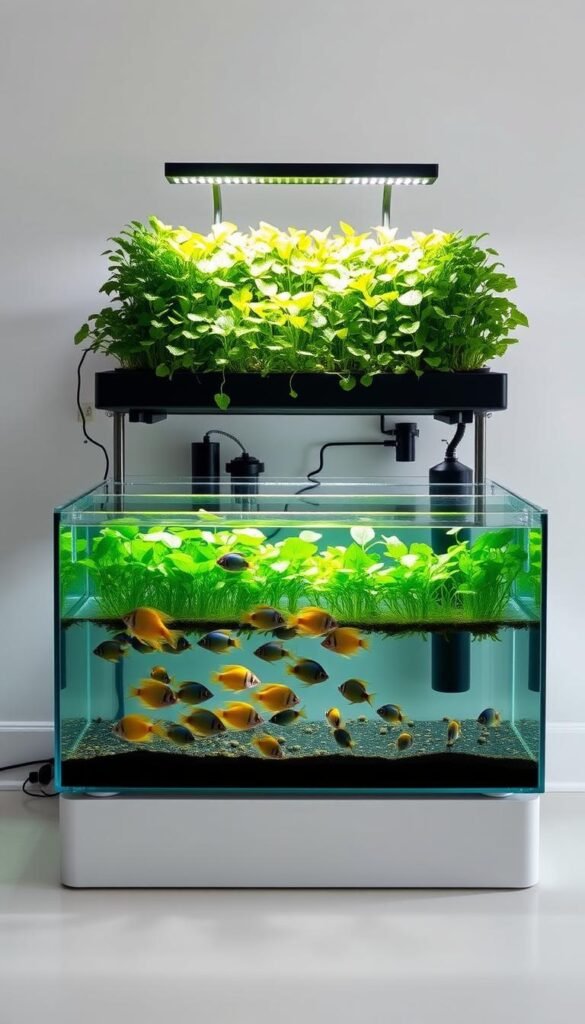
Imagine growing crisp lettuce and juicy tomatoes while raising fresh fish – all in one system. Aquaponics blends aquaculture and hydroponics, creating a closed-loop ecosystem where fish and plants thrive together. This method uses 90% less water than traditional gardening, making it perfect for eco-conscious growers.
Here’s how it works: fish waste provides natural fertilizer for your crops. In return, plants filter the water, keeping your aquatic friends healthy. No soil, no chemical additives – just pure, organic results year-round. Many urban farmers and hobbyists report doubling their harvests with minimal effort.
This guide will show you how to build a cost-effective system using common materials. You’ll discover which fish species grow fastest and what crops perform best in water-based environments. Whether you’re adding to an existing garden or starting fresh, aquaponics offers a smart solution for sustainable food production.
Key Takeaways
- Combines fish farming and soil-free plant cultivation
- Uses 90% less water than traditional gardening
- Creates natural fertilizer through fish waste
- Simplifies organic food production at home
- Works in small spaces and various climates
- Reduces maintenance through self-cleaning cycles
Getting Started with Aquaponics
Aquaponics might be the eco-friendly solution your green space needs. This method creates a closed-loop partnership between fish and crops, letting nature do most of the work. You’ll use 90% less water than soil-based gardening while harvesting both protein and produce.
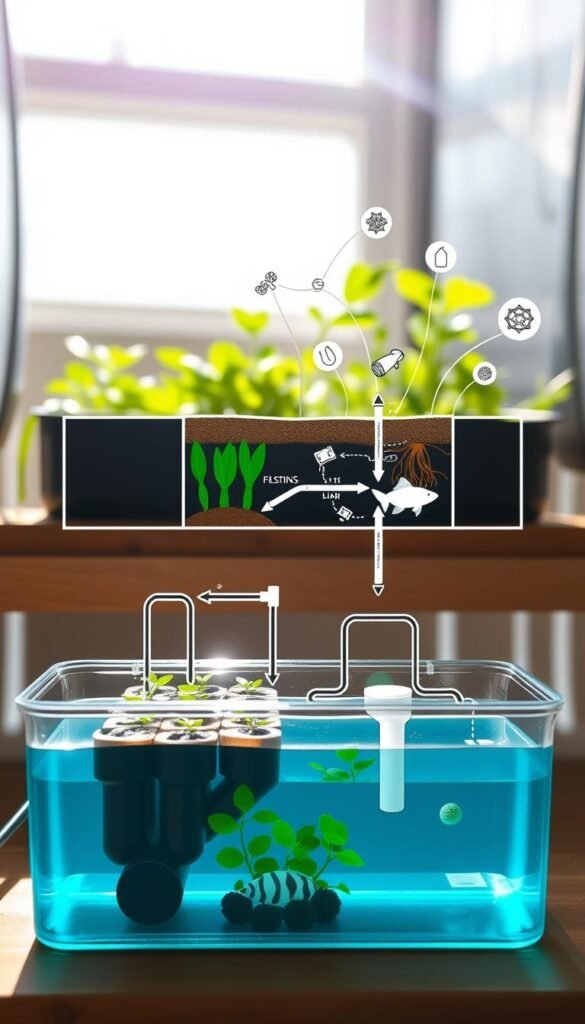
Understanding the Basics
Fish tanks and grow beds form the core of these systems. As fish produce waste, bacteria convert it into plant food. Your greens then filter the water, which cycles back clean. This natural process eliminates synthetic fertilizers and constant watering.
Key Benefits for Your Garden
Three main advantages make aquaponics stand out:
| Feature | Traditional Gardening | Aquaponics |
|---|---|---|
| Water Use | High | Low |
| Chemical Needs | Frequent | None |
| Space Efficiency | Large plots | Vertical options |
Start by measuring your available area – even a 4x4ft spot works. Popular guides and books recommend beginning with leafy greens like kale and hardy fish like tilapia. Most setups become self-sufficient within 6-8 weeks.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Aquaponics
Aquaponics thrives on a natural cycle that benefits both fish and plants. This closed-loop setup mimics nature’s way of recycling resources, letting you grow food without soil or synthetic additives. Think of it as a mini-ecosystem where every component plays a vital role.
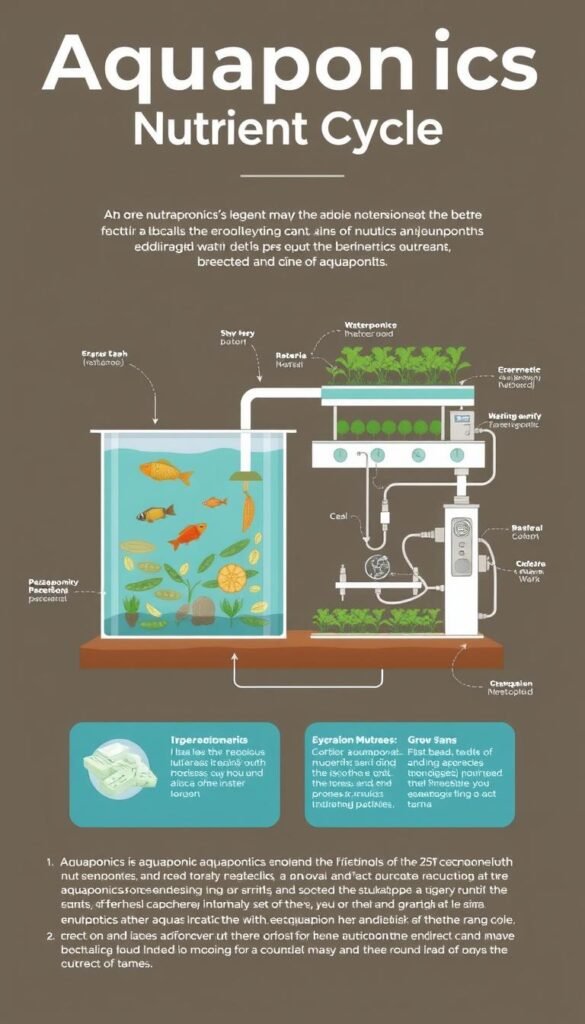
What Is Aquaponics?
An aquaponic system combines fish tanks with plant beds. Fish produce waste containing ammonia, which bacteria convert into nitrates. These nutrients feed your greens, while plants clean the water for the fish. It’s teamwork at its finest – no chemicals needed.
How the Nutrient Cycle Works
The process starts in the fish tank. As your fish eat, they release waste into the water. Helpful bacteria then break down ammonia from the waste into nitrites and nitrates. Plants absorb these nutrients through their roots, filtering the water before it returns to the tank.
Here’s why this matters:
- Tilapia or goldfish work well for beginners
- Leafy greens like basil grow fastest in these systems
- Balanced pH levels keep both fish and plants healthy
Commercial farms and backyard setups use the same basic principles. A small home system can produce herbs and veggies year-round, even in apartments. Once established, the cycle runs smoothly with minimal input – just feed the fish and watch your garden thrive.
Choosing the Right Aquaponics System
Picking the perfect setup shapes your success in raising fish and crops together. Two popular designs dominate home setups: media-based systems and raft configurations. Each excels in different environments, so let’s break down their strengths.
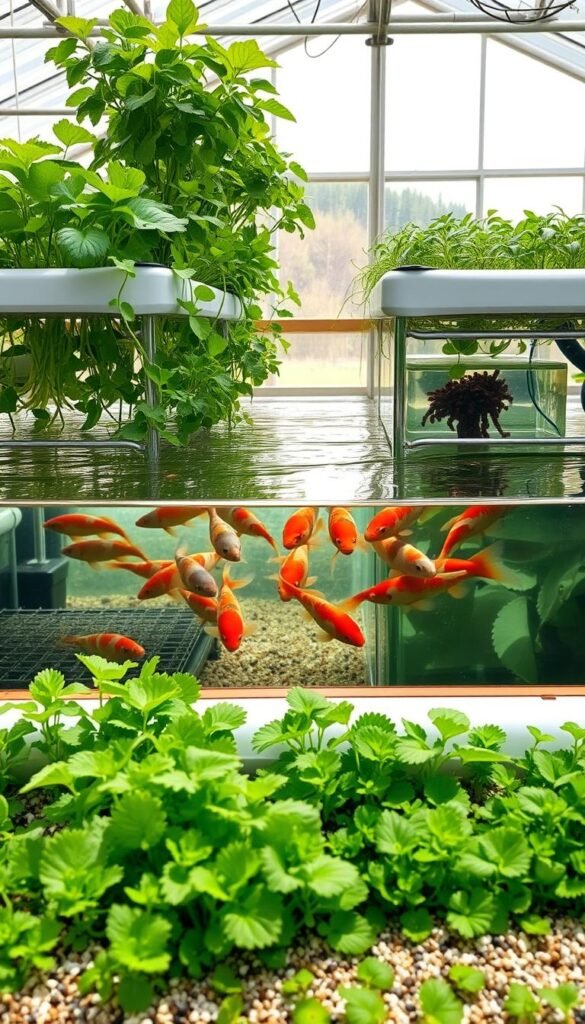

Media-Based Systems vs. Raft Systems
Media beds use gravel or clay pellets to support plant roots while filtering water. They’re ideal for small spaces and beginners – the media provides stability for herbs like basil and mint. These systems handle uneven nutrient distribution well, making them forgiving for first-timers.
Raft systems float plants on polystyrene boards above fish tanks. They require more space but grow leafy greens faster. Commercial growers favor this method for lettuce and kale production. Water circulation needs precise management here to prevent root rot.
| Feature | Media-Based | Raft |
|---|---|---|
| Space Needed | Compact (4x4ft) | Larger (8ft+) |
| Best For | Herbs & flowers | Leafy greens |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate |
Consider your goals: Want fresh food daily? Raft systems deliver constant harvests. Limited on space? Media beds fit balconies perfectly. Both designs rely on consistent water flow – invest in a reliable pump to keep nutrients moving.
Start with a media bed if you’re new to aquaponics. They’re cheaper to build and teach the core principles effectively. Once comfortable, expand with raft components for diversified crops. Your system should grow as your skills do!
Expanding Your Garden with Aquaponics: A Step‑by‑Step Guide
Smart design turns any space into a productive food hub. Start by sketching your available area – even a balcony corner works. Measure twice to avoid shipping delays for oversized components. Vertical designs maximize yields in tight spots, while ground-level setups simplify maintenance.
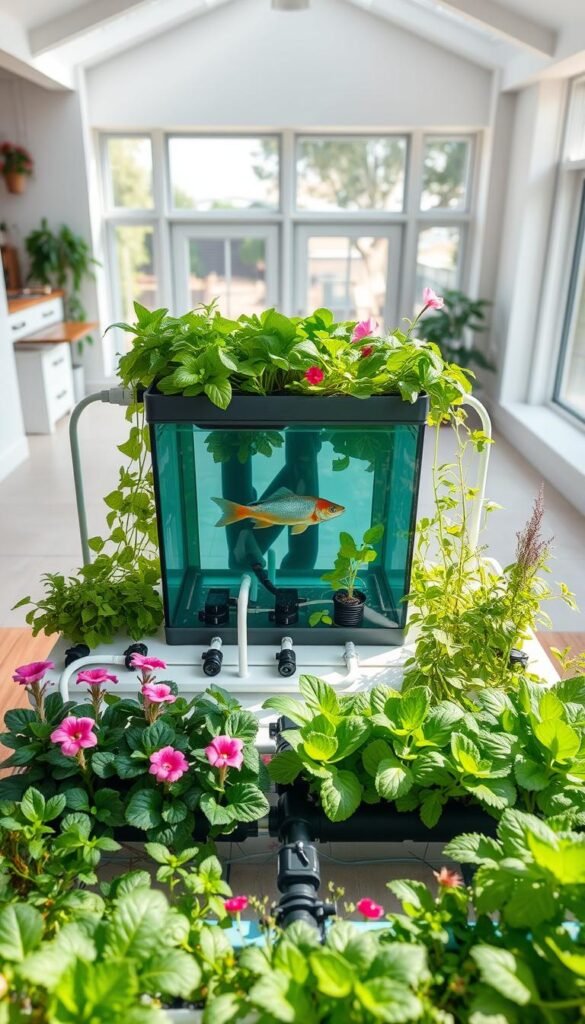

Planning Your Layout and Design
Map sunlight patterns first. Leafy greens need 4-6 hours daily, while fish tanks thrive in shaded areas. Use graph paper or free apps to visualize pipe routes and grow bed placements. Pro tip: Leave 18″ walkways for easy harvesting and system checks.
Gathering Essential Tools and Materials
Build your shopping list with these basics:
- Food-grade fish tanks (50-100 gallon)
- PVC pipes for water circulation
- Clay pebbles or raft boards
- pH testing kit
Check product reviews before buying pumps – look for models with ≤40 decibel noise. Local farm stores often beat online shipping costs for bulky items. Bookmark reliable sites with information on organic fish feed options to streamline future orders.
Selecting the Best Fish and Plants for Your System
Your aquaponics system’s success starts with smart pairings. Choosing compatible species creates a balanced ecosystem where both fish and crops flourish. Let’s explore beginner-friendly options that thrive in various setups.
Choosing Hardy Fish for Beginners
Start with resilient swimmers that tolerate water fluctuations. Tilapia tops the list – they grow fast and handle temperature changes well. Goldfish and koi also adapt easily, making them perfect for first-time setups.
| Fish Type | Ideal Temp | Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Tilapia | 75-85°F | Vegetable pellets |
| Goldfish | 65-75°F | Algae & flakes |
| Koi | 60-75°F | Protein-rich mix |
Order fish from reputable breeders – check customer reviews and compare images before purchasing. A local supplier often provides healthier stock than large-scale business operations.
Identifying Ideal Plants for Growth
Leafy greens dominate water-based gardens. Lettuce varieties grow rapidly, while herbs like basil add flavor diversity. Avoid root vegetables initially – they need more developed systems.
| Plant Type | Growth Time | Nutrient Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Butterhead Lettuce | 3-4 weeks | Moderate |
| Basil | 5-6 weeks | High |
| Swiss Chard | 6-8 weeks | Low |
Design tip: Place fast-growing plants near water inlets for maximum nutrient access. Monitor pH levels weekly – most greens prefer 6.0-7.0 ranges. With time, you’ll learn which combinations yield the best harvests for your space and goals.
“Match fish waste production to plant consumption – it’s the golden rule for system balance.”
Setting Up Your Aquaponics System at Home
Transforming unused space into a thriving ecosystem begins with smart setup choices. Proper positioning and component selection ensure your system operates smoothly from day one. Let’s walk through the essentials for creating a safe, productive environment.
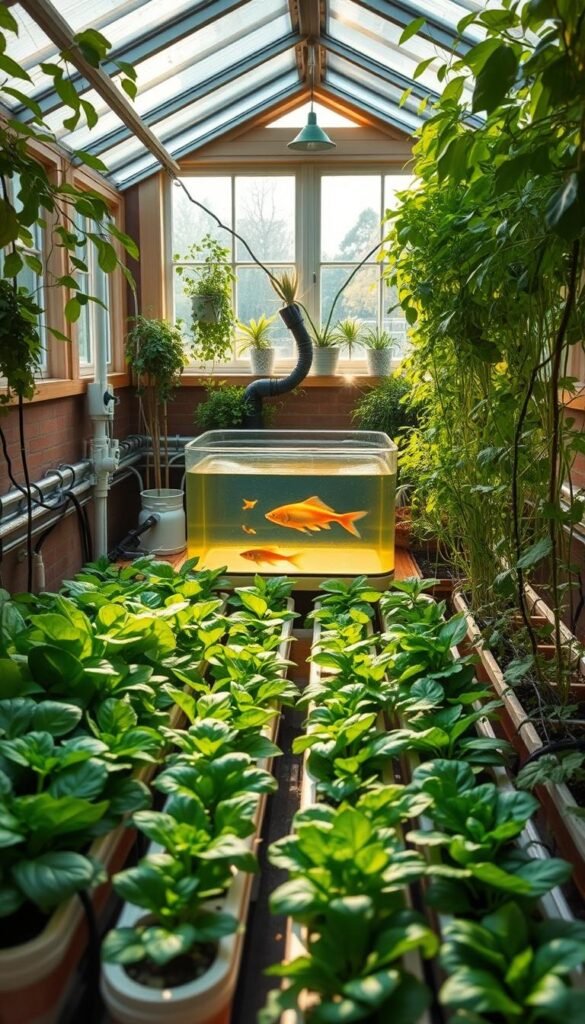

Assembly Sequence Made Simple
- Position the fish tank on a flat, shaded surface – garages or covered patios work well
- Elevate grow beds 12-18″ above the tank using sturdy shelving
- Connect PVC pipes using slip-resistant fittings for leak-free water flow
Always review pump specifications before installation. Submersible models work best for small setups, while external pumps suit larger systems. Test connections with water before adding fish or plants to catch leaks early.
Safety comes first in these three areas:
- Secure tanks against tipping with wall brackets
- Use GFCI outlets for electrical components
- Wear gloves when handling clay grow media
| Pump Type | Flow Rate | Noise Level |
|---|---|---|
| Submersible | 200 GPH | Quiet |
| External | 500 GPH | Moderate |
Consider your view of the system when planning – you’ll want easy access for daily checks. Many beginners find vertical designs save space while maintaining visual appeal. Multiple options exist for oxygenation: air stones work for small tanks, while venturi injectors better suit complex setups.
“Double-check every connection during dry runs – prevention beats troubleshooting later.”
Maintaining and Monitoring Your Aquaponics System
Keeping your aquaponics system thriving requires regular checkups and smart adjustments. Think of it like a living clock – every gear (fish, plants, and bacteria) must work in sync. A weekly routine prevents small issues from becoming big headaches.
Water Quality and pH Management
Test water every Monday and Thursday with digital meters or test strips. Ideal ranges:
| Parameter | Fish Safety | Plant Growth |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | 6.8-7.2 | 6.0-7.0 |
| Ammonia | <0.5 ppm | – |
| Nitrates | – | 20-50 ppm |
Use baking soda to raise pH or vinegar to lower it. Add oxygen stones if fish gasp at the surface. For greenhouse setups, monitor humidity – high moisture can alter water chemistry.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Algae blooms? Cut light exposure with shade cloth. Root rot? Check water flow in grow beds. This step guide raising healthy crops includes:
- Monthly pipe flushes with filtered water
- Trimming dead plant matter weekly
- Inspecting pump filters every 10 days
Spot aphids? Spray neem oil – it’s fish-safe. For cold climates, use greenhouse covers to maintain stable temps. Most problems fix quickly when caught early.
“Balance is everything – your pH levels tell the system’s story before issues appear.”
Follow this guide raising vegetables and fish together by tracking three numbers: pH, ammonia, and nitrate levels. Log results in a notebook to spot trends. Systems often stabilize after 2-3 months, requiring less frequent checks.
Optimizing Your Aquaponics Garden for Success
Fine-tuning your setup unlocks hidden potential in every square foot. Like adjusting a recipe, small changes to your aquaponics system can dramatically improve plant growth and fish health. Let’s explore how to create perfect harmony between your crops and aquatic partners.
Enhancing System Efficiency
Balance begins with nutrient distribution. Test water weekly to ensure ammonia levels stay below 0.5 ppm – crucial for raising vegetables and fish safely. If lettuce grows slowly, add more goldfish or adjust feeding schedules to boost nitrogen output.
Three proven upgrades maximize productivity:
- Install spiral water flow patterns in grow beds
- Add supplemental LED lighting for faster photosynthesis
- Use airlift pumps instead of electric models
| Upgrade | Cost | Yield Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical grow towers | $40 | 35% |
| Automated pH monitor | $75 | 28% |
| Sludge separator | $120 | 42% |
Urban farmers in Phoenix doubled tomato yields by painting their fish tanks white – simple reflectors redirected sunlight to shaded plants. Track growth rates and water clarity as key indicators. When both improve, you’ve nailed the sweet spot for aquaponic gardening.
“Our kale production tripled after adding a simple swirl filter – it’s all about working smarter, not harder.”
Practical Tips for Long‑Term Sustainability
Sustaining an aquaponics system long-term requires smart habits that protect your fish and crops. Start by mastering feeding routines – overfed fish create water imbalances, while underfed ones starve your plants. Follow this golden rule: offer only what your fish consume in 5 minutes, twice daily.
These three fish food strategies keep nutrients flowing smoothly:
- Use floating pellets to monitor consumption easily
- Supplement with duckweed for natural protein
- Fast fish one day weekly to prevent waste buildup
| Food Type | Protein % | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Pellets | 32-40 | Daily feeding |
| Black Soldier Fly Larvae | 42 | Growth spurts |
| Homegrown Duckweed | 25 | Budget systems |
Seasonal changes demand adjustments. Add aquarium heaters before winter if raising tilapia. In summer, shade tanks to prevent algae blooms. Test water weekly – ammonia spikes often signal fish food issues or pump failures.
New enthusiasts need know these maintenance essentials:
- Scrub grow bed surfaces monthly
- Replace 10% water weekly
- Inspect pipe joints quarterly
“Consistency beats intensity – fifteen daily minutes of observation prevents 90% of system crashes.”
With these basics aquaponics practices, your setup becomes self-reinforcing. Track progress in a journal: note harvest weights, fish growth rates, and repair costs. Small tweaks compound into major improvements over seasons.
Conclusion
Transforming your backyard into a sustainable food source becomes simple with aquaponics. You’ve learned how to balance raising fish and crops in one efficient loop – from choosing hardy tilapia to optimizing leafy green growth. This method cuts water use dramatically while delivering organic results.
Remember: success starts with proper setup and weekly water checks. Many beginners find detailed guide helpful for troubleshooting pH swings or algae issues. Pair your progress with customer reviews of pumps and grow media – real-world insights prevent costly mistakes.
Your journey doesn’t end here. Track harvests, adjust feeding schedules, and experiment with new plant varieties. Those mastering aquaponics gardening often share one tip: stay curious. Small tweaks based on system performance can double yields over time.
Ready to dive deeper? Compare customer reviews of vertical grow towers or automated monitors. Every upgrade brings you closer to a self-sustaining ecosystem where raising fish fuels endless harvests. Start small, learn continuously, and watch your edible oasis thrive.






