Growing lush greens without soil might seem like magic, but success comes down to science. Balancing your system’s chemistry directly impacts whether your crops absorb vitamins and minerals effectively. Get it right, and you’ll see faster growth, brighter colors, and higher yields.
Plants in water-based setups rely entirely on what you provide. Research shows roots absorb iron best at 5.5-6.5 ranges, while calcium prefers slightly higher zones. Too acidic or alkaline? Essential elements become locked away, starving your greens even in a nutrient-rich solution.
This guide walks through simple tools and techniques for testing your setup. You’ll learn how to spot imbalances early and make adjustments using household items or digital meters. We’ll also share real-world examples of growers who doubled harvests by refining their approach.
Think of your nutrient solution as a personalized meal plan for your plants. Just like humans need varied diets, different crops thrive under specific conditions. Lettuce prefers slightly acidic environments, while basil grows stronger in neutral zones. Tailoring your care ensures every leaf reaches its full potential.
What is pH and Why It Matters in Hydroponics?

Think of pH as your plants’ dietary translator. Just like you need the right spices to enjoy a meal, roots require specific chemical conditions to “taste” nutrients. This invisible factor determines whether your crops feast or starve – even in a perfectly mixed solution.
Defining pH and the pH Scale
The pH scale runs from 0 to 14, measuring how acidic or alkaline your water is. A reading of 7 is neutral – think pure water. Numbers below 7 mean acidity (like vinegar), while values above indicate alkalinity (similar to baking soda). But here’s the kicker: it’s logarithmic. A pH of 5 is 10 times more acidic than 6!
Acidity vs. Alkalinity in Nutrient Solutions
Most hydroponic systems thrive between 5.5 and 6.5. Why? Essential minerals dissolve best in this range. Iron becomes 80% more available at pH 6 versus 7. Calcium prefers slightly higher zones. Get it wrong, and nutrients form insoluble compounds – like trying to drink a milkshake through a coffee stirrer.
Testing tools make all the difference:
- Digital meters give precise readings
- Litmus paper offers quick checks
- Liquid test kits work for budget growers
Stray outside the sweet spot, and you’ll see leaf discoloration or stunted growth. That’s when troubleshooting common hydroponic issues becomes crucial. Regular checks prevent minor imbalances from becoming crop disasters.
Understanding pH Levels: Key to Healthy Hydroponic Plants

Your plants’ journey from seedling to harvest depends on a chemical balancing act. Research reveals that nutrient absorption rates swing dramatically across pH ranges – up to 300% differences for elements like manganese. Strawberry growers report 40% yield boosts when maintaining 5.8-6.2 levels during fruiting phases.
Young plants crave slightly acidic conditions (5.5-6.0) to access nitrogen for leaf development. As they mature, a gradual shift toward 6.0-6.5 improves calcium uptake for sturdy stems. Commercial lettuce farms time these adjustments weekly, mirroring natural soil changes.
| Growth Stage | Ideal pH Range | Key Nutrients Accessed |
|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 5.5-6.0 | Nitrogen, Phosphorus |
| Vegetative | 5.8-6.3 | Potassium, Magnesium |
| Flowering | 6.0-6.5 | Calcium, Sulfur |
Tomato growers learned this the hard way – flowers dropped prematurely at pH 5.2 until they added potassium hydroxide. Now they test thrice weekly, aligning with hydroponic gardening system maintenance tips from extension services. Your nutrient solution isn’t “set and forget” – it’s a living recipe that evolves with each growth spurt.
University trials show pH impacts not just quantity, but quality. Basil grown at 6.0 contains 15% more essential oils than at 5.0. By tracking your hydroponic system daily during peak growth, you become a plant nutrition maestro – mixing the perfect chemical cocktail for every life chapter.
Optimal pH Ranges for Hydroponic Systems

Finding the perfect pH zone for your plants is like tuning a guitar – slightly off, and the whole performance suffers. Most water-based setups thrive between 5.5 and 6.5, where roots easily access essential minerals. But just as tomatoes crave different care than kale, your nutrient solution needs customization.
Sweet Spot for Success
Leafy greens like spinach and lettuce flourish at 5.5-6.0, absorbing iron and manganese efficiently. Fruiting crops prefer 6.0-6.5 for better calcium uptake. Rockwool users – soak your media in pH-balanced water first! Untreated fibers can push levels upward, throwing your system off track.
Customizing for Your Crops
Tomato vines show their gratitude for a 5.8-6.0 range during flowering with plumper fruits. Herbs like basil stay vibrant near 6.5. Use pH-down solutions (phosphoric acid) or pH-up products (potassium hydroxide) to fine-tune your mix. Always adjust gradually – sudden shifts shock roots like ice water on bare feet.
Testing every 2-3 days keeps nutrients available and plants thriving. Remember: your hydroponic setup isn’t just growing plants – it’s crafting a mineral buffet where every element gets a seat at the table.
The Science Behind Nutrient Absorption and pH
Plants in hydroponic systems aren’t picky eaters – they’re prisoners of their environment’s chemistry. The nutrient solution you provide acts like a master key, unlocking minerals only when pH levels align with each element’s preferences. Get this balance wrong, and your greens might starve beside a full buffet.
How pH Affects Macronutrient and Micronutrient Uptake
Macronutrients like nitrogen and potassium behave differently than trace elements. At pH 6.0, plants absorb nutrients like phosphorus 30% faster than at 7.0. Iron availability plummets 80% when solutions turn too alkaline. Here’s the twist: each mineral has its own pH sweet spot.
| Nutrient | Type | Optimal pH Range | Absorption Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | Macro | 5.5-6.5 | 85% |
| Iron | Micro | 5.0-6.0 | 70% |
| Calcium | Macro | 6.0-6.8 | 90% |
Tomato growers see this play out dramatically. During vegetative growth, plants crave lower pH (5.8-6.0) for nitrogen uptake. When flowers form, raising to 6.2-6.5 boosts calcium absorption by 40% – preventing blossom-end rot.
Balancing Nutrient Solutions for Growth
Your mixing routine should mirror nature’s rhythms. Start with a base solution at pH 5.8 for seedlings. Gradually increase to 6.3 as plants mature. Weekly adjustments prevent lockouts – think of it as tuning a radio dial for crystal-clear reception.
Hydroponics pros use these tricks:
- Test solutions 2 hours after feeding
- Adjust in 0.5 increments daily
- Flush systems monthly to reset mineral buildup
One commercial lettuce farm doubled yields by cycling between 5.5 and 6.2 weekly. Their secret? Matching pH shifts to the plants’ internal nutrient clocks. Your crops will thank you with lusher leaves and heartier fruits.
How to Test and Monitor pH in Your Hydroponic System
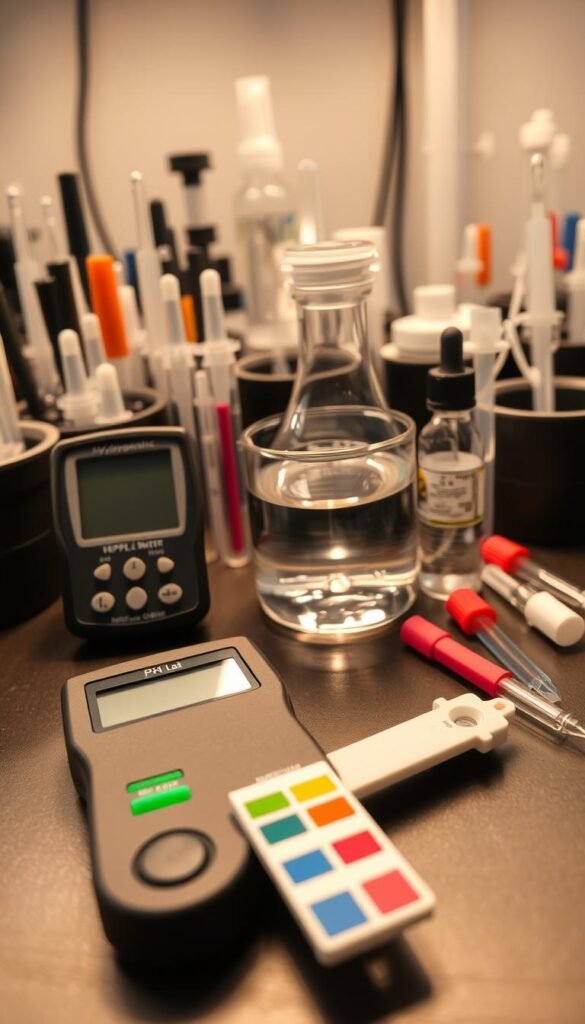

Your hydroponic garden’s success starts with precise measurements. Choosing the right tools ensures your plants access nutrients effectively. Let’s explore two popular methods for tracking chemical balance in water-based setups.
Digital pH Meters vs. Litmus Test Strips
Digital meters deliver lab-grade accuracy but require regular care. They’re ideal for large systems needing frequent checks. Litmus strips offer instant results at lower costs – perfect for quick assessments. Consider these factors:
- Meters: Last 2-3 years with calibration • $30-$100 initial cost
- Strips: Disposable • $10 per 100 tests • ±0.5 pH margin
Commercial growers prefer meters for reliability. Hobbyists often mix both – using strips for daily scans and meters for weekly deep dives.
Calibration and Regular Monitoring Tips
Calibrate digital tools weekly with buffer solutions (4.0, 7.0, 10.0). Follow these steps:
- Rinse probe in distilled water
- Dip into calibration fluid
- Adjust until display matches known value
Test your nutrient solution every 48 hours. Always check after adding fertilizers – mineral blends can shift balance rapidly. Store meters upright in storage solution to prolong sensor life.
Consistent tracking catches issues before yellow leaves appear. Pair testing with water quality checks – hard water requires more frequent adjustments. Your plants will reward the vigilance with vibrant growth.
Adjusting pH in Your Hydroponic Nutrient Solution
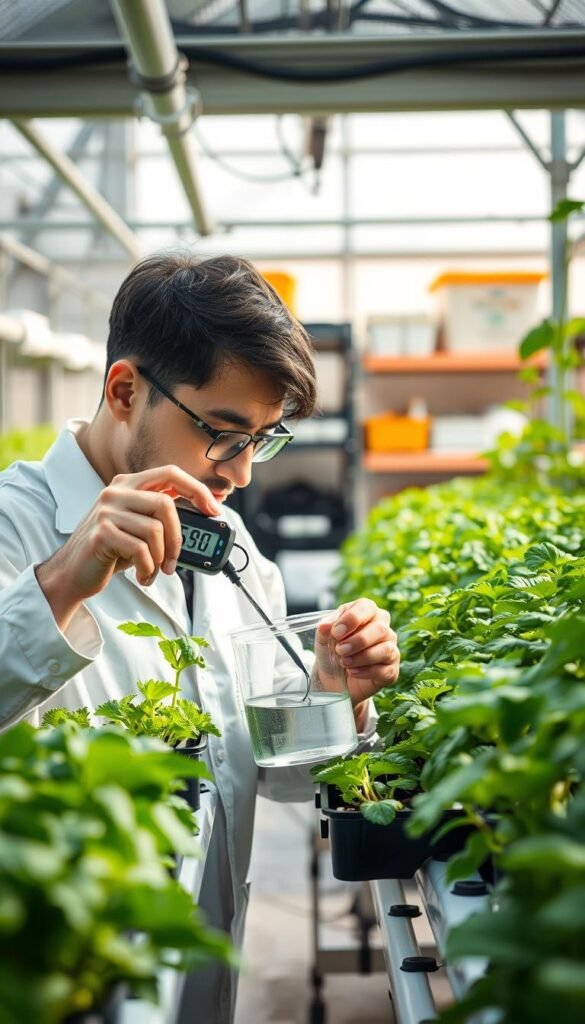

Mastering pH adjustments transforms your hydroponic garden from guesswork to precision farming. Commercial-grade pH-up and pH-down products act like chemical dials, letting you fine-tune your solution with surgical accuracy. Trusted brands like General Hydroponics offer concentrated formulas that work 3x faster than DIY methods.
Step-by-Step Use of pH-Up and pH-Down Products
Start with clean gloves and goggles – these acid-based solutions demand respect. Follow this battle-tested process:
- Test your nutrient mix 30 minutes after adding fertilizers
- Add 1 mL of pH-down (phosphoric acid) per gallon to lower levels
- Use 0.5 mL of pH-up (potassium hydroxide) per gallon to raise
- Wait 15 minutes, then retest
Never exceed 2 mL per gallon in a single adjustment. One urban farm ruined 200 basil plants by adding 5 mL of pH-down directly to roots – always dilute in water first!
Best Practices for Gradual Adjustments
Plants hate sudden chemical shocks more than you dislike burnt coffee. Limit daily shifts to 0.5 pH units maximum. Here’s why:
| Adjustment Speed | Root Stress Level | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5/day | Low | 12-24 hours |
| 1.0+/day | High | 3-5 days |
Alternate methods work too. Some growers use citric acid for gentle pH reductions. Others employ automated dosers for round-the-clock stability. Whatever system you choose, consistency beats perfection every time.
Test your solutions at the same hour daily – temperature swings alter readings. Found a 1.0 pH jump overnight? Check for algae growth or expired nutrients. Your plants will thrive when adjustments feel like subtle nudges, not seismic shifts.
Impact of Water Quality and Reverse Osmosis on pH

Water is the silent partner in your hydroponic garden, shaping chemical balance behind the scenes. What flows from your tap isn’t just H₂O – dissolved minerals like calcium and magnesium carbonate play hide-and-seek with your nutrient mix. These invisible guests determine whether your solution stays stable or swings like a pendulum.
Understanding Water Hardness and Buffering Capacity
Hard water contains high mineral levels that act like pH bodyguards. Carbonates resist changes, making adjustments frustrating. A solution might bounce back to 7.5 overnight despite adding pH-down. Soft water lacks this buffering power, requiring fewer corrections but offering less natural stability.
Scale buildup in pipes and pumps signals trouble. White crusty deposits reduce flow rates and clog emitters over time. Temperature swings worsen this – warmer water holds more dissolved minerals that crash out as solids when cooled. Test your source before mixing nutrients using:
- TDS meters to measure total dissolved solids
- GH/KH test kits for carbonate hardness
- Digital thermometers to track temperature shifts
Reverse osmosis systems strip 90-99% of minerals, giving you a clean slate. While RO units cost $150-$300 upfront, they prevent endless pH battles. Always adjust filtered water’s pH before adding fertilizers – additives like calcium nitrate shift levels unpredictably.
Commercial growers using RO report 30% fewer pH corrections weekly. Your plants get exactly what you intend, not what your local water board decided. Remember: consistency in water quality means predictability in growth.
Timing and Frequency of pH Adjustments
Keeping your hydroponic garden thriving is all about rhythm. Like a well-timed dance, checking and adjusting your system’s chemical balance ensures nutrients flow smoothly to roots. Get the tempo wrong, and your greens might stumble.
Start by testing every time you mix fresh nutrients. Solutions often drift as minerals dissolve – a batch at 6.0 today could hit 6.8 tomorrow. Top off reservoirs? Test again. Added water dilutes the mix, potentially skewing levels.
Growth stages dictate your schedule:
- Seedlings: Check daily – young roots are sensitive
- Vegetative phase: Test every 2-3 days
- Flowering/fruiting: Weekly checks suffice
Plants themselves influence this rhythm. As they absorb nitrogen, solutions become more alkaline. Calcium-heavy diets? Acidity creeps up. One tomato grower shared how their reservoir jumped 0.8 pH units in 48 hours during peak fruiting.
Environmental factors add twists. Warm rooms accelerate evaporation, concentrating minerals. Cool nights? Roots absorb less, leaving excess nutrients. Track these patterns like a weather forecast – adjust your testing frequency accordingly.
Set phone reminders for checks if you’re forgetful. Many gardeners pair pH tests with morning nutrient top-offs. Consistency matters more than perfection – small, regular tweaks keep your plant’s buffet table fully stocked.
Environmental Factors Affecting pH in Hydroponics
Your hydroponic garden’s environment acts like an invisible puppeteer, pulling strings that control nutrient availability. Three key players – temperature swings, light intensity, and microbial life – can turn your carefully balanced solution into a nutritional minefield.
Temperature, Light, and Evaporation Effects
Warm rooms accelerate evaporation, concentrating minerals and raising pH levels. For every 10°F increase, nutrient solutions can become 0.3 units more alkaline. Grow lights add heat – LED setups cause smaller shifts than HPS bulbs. A pepper grower in Arizona saw daily pH spikes from 5.8 to 7.1 until installing cooling fans.
Light duration matters too. Plants absorbing nutrients under 18-hour cycles alter solution chemistry faster than those in 12-hour schedules. Monitor reservoirs morning and evening during heatwaves – daily swings over 1.0 pH unit signal trouble.
Influence of Microbial Activity and Media
Beneficial bacteria in clay pellets or coco coir produce acids that lower pH naturally. But harmful microbes? They create alkaline byproducts. One basil farm discovered root zone pH jumping to 7.8 from contaminated grow stones, causing iron deficiencies.
Media choices impact stability:
- Rockwool initially raises pH
- Lava rock buffers against sudden changes
- Perlite offers minimal interaction
Pre-soak media in pH-balanced water for 24 hours. Check runoff weekly – discrepancies over 0.5 units mean adjustments are needed. Your gardening success hinges on recognizing these invisible influencers before deficiencies yellow leaves or stunt growth.
Expert Tips and Best Practices for pH Management
Mastering pH control separates thriving hydroponic gardens from struggling setups. Even experienced growers face challenges – a 2023 survey revealed 68% of crop failures stem from improper chemical balance. Let’s explore how to sidestep common errors and maintain stability.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Rookie mistakes often start with inconsistent testing. Using expired strips or uncalibrated meters gives false readings – like driving with a broken speedometer. One basil farmer lost 30 plants by trusting a $5 test kit that hadn’t been updated in 6 months. Invest in a quality digital meter and check calibration weekly.
Other frequent errors:
- Adjusting levels too quickly (more than 0.5 daily)
- Ignoring water temperature during tests
- Forgetting to account for nutrient absorption rates
Maintaining Consistent Nutrient and pH Levels
Your system’s performance depends on routine. Test solutions at the same time daily – morning readings often differ from evening checks by 0.3 units. Keep a logbook tracking adjustments and plant responses. Commercial growers using this method reduce correction frequency by 40% within 3 months.
Consider these options for stability:
- Automated dosing systems for large setups
- Buffered nutrients that resist pH swings
- Weekly reservoir flushes to reset mineral buildup
New to hydroponic gardening for beginners? Start with pre-mixed solutions and gradually experiment with custom blends. Your plants’ growth patterns will guide refinements – yellowing leaves often signal needed adjustments before meters do.
Final Thoughts on Optimizing pH for Thriving Hydroponic Gardens
Mastering your garden’s invisible chemistry unlocks its full potential. Proper balance ensures roots access every nutrient you provide, transforming water into a supercharged growth elixir. Regular testing and gradual adjustments become your secret weapons against deficiencies.
Customizing solutions for specific crops pays dividends. Leafy greens demand different care than fruit-bearing plants – track their needs like a nutritionist crafting meal plans. Digital meters and consistent routines simplify maintenance, letting you focus on growth rather than guesswork.
Healthy systems start with awareness. Check reservoirs often, especially after adding fertilizers or water. Small tweaks prevent drastic swings, keeping plants stress-free. Remember: thriving gardens aren’t accidents – they’re built through attentive, science-backed care.
Ready to see results? Apply these strategies to your hydroponic system today. Your greens will reward you with vibrant leaves, robust yields, and resilience against common issues. Start small, stay consistent, and watch your growing plants outshine soil-based rivals.






